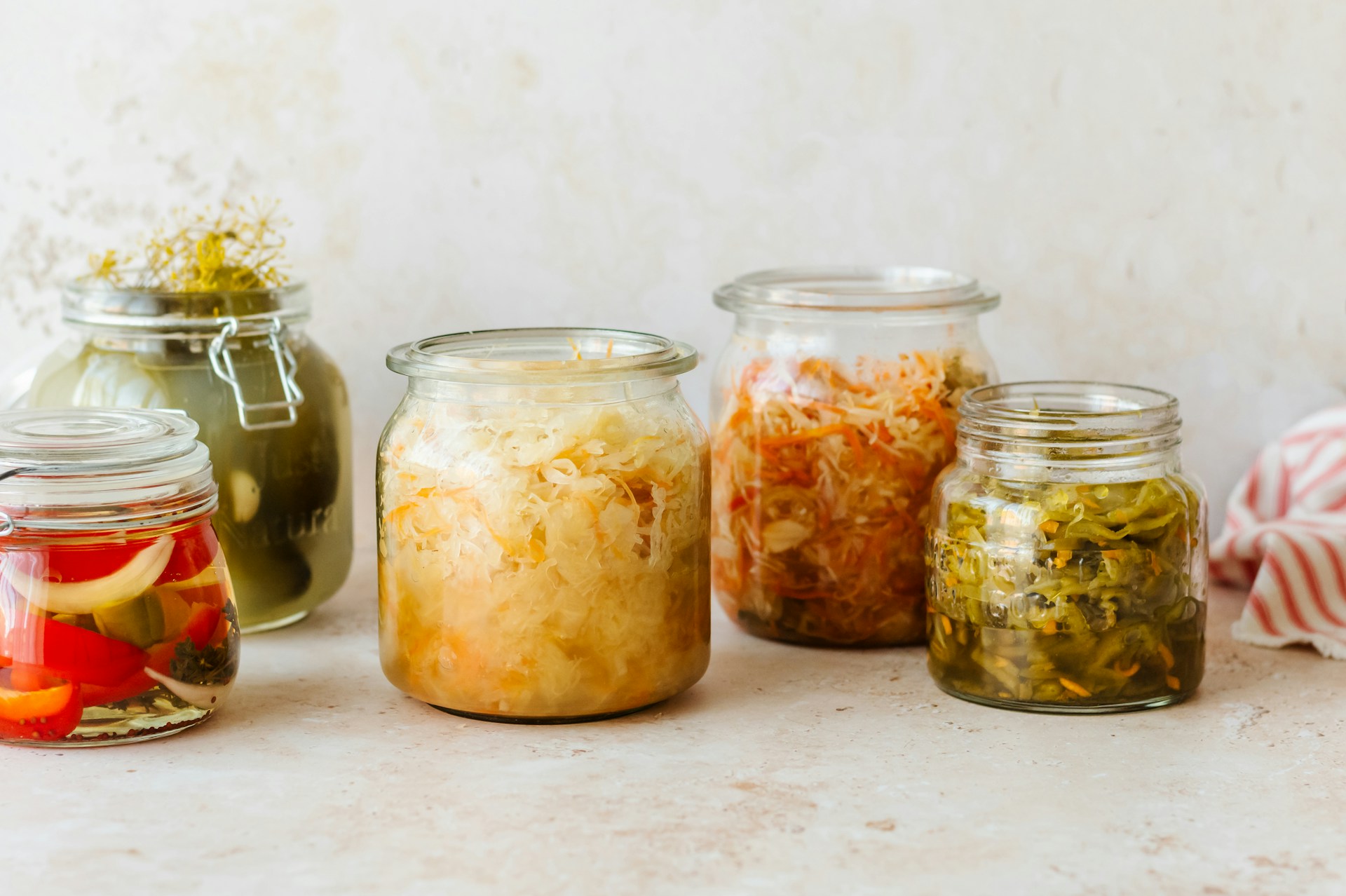
The discussions surrounding gut health have intensified in recent years, especially as new research sheds light on its crucial role in overall health. One recent study conducted by a team of nephrologists in China highlights how live microorganisms in our diets may influence the risk of developing chronic kidney disease (CKD). This compelling connection draws attention to the importance of what we consume.
The Prevalence of Chronic Kidney Disease
Chronic kidney disease affects approximately 10% of adults globally, translating to more than 35 million Americans. Alarmingly, projections suggest it will become one of the leading causes of death by 2040. Given that there is no effective treatment currently available, finding preventive strategies is more crucial than ever.
Insights from Research
The study published in Renal Failure analyzed data from the National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey, encompassing over 12,000 participants. The researchers categorized these individuals based on their intake of live microbial foods, emphasizing the distinctions between low, moderate, and high consumption levels.
1. Low Microbial Intake: Individuals who consume little to no live microbial foods.
2. Moderate Microbial Intake: Those who include some moderate levels but no high levels of live microbial foods.
3. High Microbial Intake: Participants who consume a significant amount of high live microbial foods.
4. Moderate/High Microbial Intake: Those consuming either moderate or high live microbial foods.
The Link Between Live Microorganisms and CKD Risk
The findings from the study were noteworthy. Individuals in the high microbial intake group exhibited a significantly lower risk of developing CKD compared to those in the low intake group. This connection adds to growing evidence that maintaining a balanced gut microbiota may be crucial in promoting kidney health.
The researchers noted that specific foods such as fermented products—cottage cheese, sauerkraut, and yogurt—are likely to contain live cultures that can benefit gut health.
A Novel Dietary Approach
The researchers concluded that incorporating a diet rich in live microorganisms could serve as a promising dietary strategy for reducing the risk of CKD. While more research is necessary to fully understand the mechanisms at play, the initial findings support the idea that dietary changes could have profound implications for kidney health.
Final Thoughts: The Importance of a Balanced Diet
For individuals concerned about kidney disease or those looking to prioritize their overall health, focusing on gut health through dietary choices makes sense. This research reinforces the idea that a balanced diet, enriched with live microorganisms, is beneficial for both gut and kidney health, forming a crucial foundation for our well-being.
By understanding the relationship between gut health and kidney disease, individuals can make informed decisions about their diets, potentially reducing their risk of chronic conditions such as CKD. Adopting simple dietary changes today may pave the way for healthier kidneys tomorrow.
Image Source: Unsplash